
Then, the COUNT(*) function returns the number of tracks for each album or group of tracks.Ĥ) SQLite COUNT(*) with HAVING clause example.

First, the GROUP BY clause group tracks by album id.
SQLITE COUNT GROUP BY EXAMPLE CODE
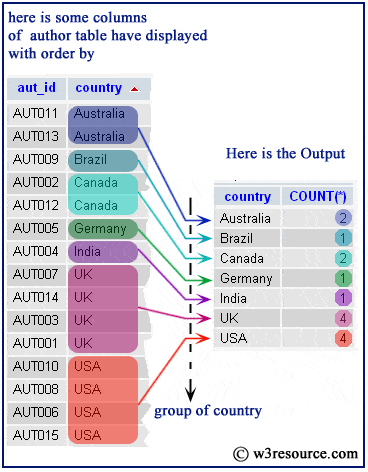
To get all the albums and the number of tracks in each album, you combine the COUNT(*) function with the GROUP BY clause: SELECTĪlbumid Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) ( sql ) WHERE albumid = 10 Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) ( sql )ġ4 3) SQLite COUNT(*) with GROUP BY clause example The following statement uses the COUNT(*) function with a WHERE clause to find the number of tracks whose album id is 10: SELECT COUNT(*) To get the number of rows from the tracks table, you use the COUNT(*) function as follows: SELECT count(*)įROM tracks Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) ( sql )ģ503 Code language: plaintext ( plaintext ) 2) SQLite COUNT(*) with WHERE clause example We will take the table tracks in the sample database to demonstrate the functionality of the COUNT(*) function. Sixth, use the COUNT(DISTINCT expression) to get the number of unique and non-null values in column c: SELECT COUNT( DISTINCT c) FROM t1 Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) ( sql ) SQLite COUNT(*) examples It counts the duplicate rows as separate rows. In this example, the COUNT(c) returns the number of non-null values. Third, query data from the t1 table: SELECT * FROM t1 Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) ( sql )įourth, use the COUNT(*) function to return the number of rows in the t1 table: SELECT COUNT(*) FROM t1 Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) ( sql )Īs you can see clearly from the output, the result set includes NULL and duplicate rows.įifth, use the COUNT(expression) to get the number of non-null values in the column c: SELECT COUNT(c) FROM t1 Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) ( sql ) VALUES( 1),( 2),( 3),( null),( 3) Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) ( sql ) Second, insert five rows into the t1 table: INSERT INTO t1(c) SQLite COUNT() function illustrationįirst, create a table called t1 that has one column: CREATE TABLE t1(c INTEGER) Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) ( sql ) The COUNT(*) function returns the number of rows in a table, including the rows including NULL and duplicates. SQLite provides another syntax of the COUNT() function: COUNT(*) Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) ( sql ) The expression can be a column or an expression that involves columns to which the function COUNT() is applied. DISTINCT: if you explicitly use the DISTINCT option, the COUNT function counts only unique and non-null values.The COUNT() function uses the ALL option by default if you skip it. ALL: when you specify all, the COUNT() function counts all non-null values include duplicates.The following describes the meanings of ALL and DISTINCT options: The COUNT function behaves according to the arguments that you pass into it and the option ALL or DISTINCT that you specify. The following illustrates the basic syntax of the COUNT function: COUNT( expression) Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) ( sql ) Arguments The function COUNT() is an aggregate function that returns the number of items in a group.įor example, you can use the COUNT() function to get the number of tracks from the tracks table, the number of artists from the artists table, and so on.
SQLITE COUNT GROUP BY EXAMPLE HOW TO
Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use SQLite COUNT function to get the number of items in a group.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
